Using git metadata
The CLI can attach git metadata like branch, commit sha, owner and more when executing the test --record and deploy commands. This way you can keep track of
your test sessions and deployed resources in the UI and cross-reference them with any updates to your code.
For example, in the screenshot below we ran a test session from our CI server after the project was deployed to our
Staging environment with the npx checkly test --record command.
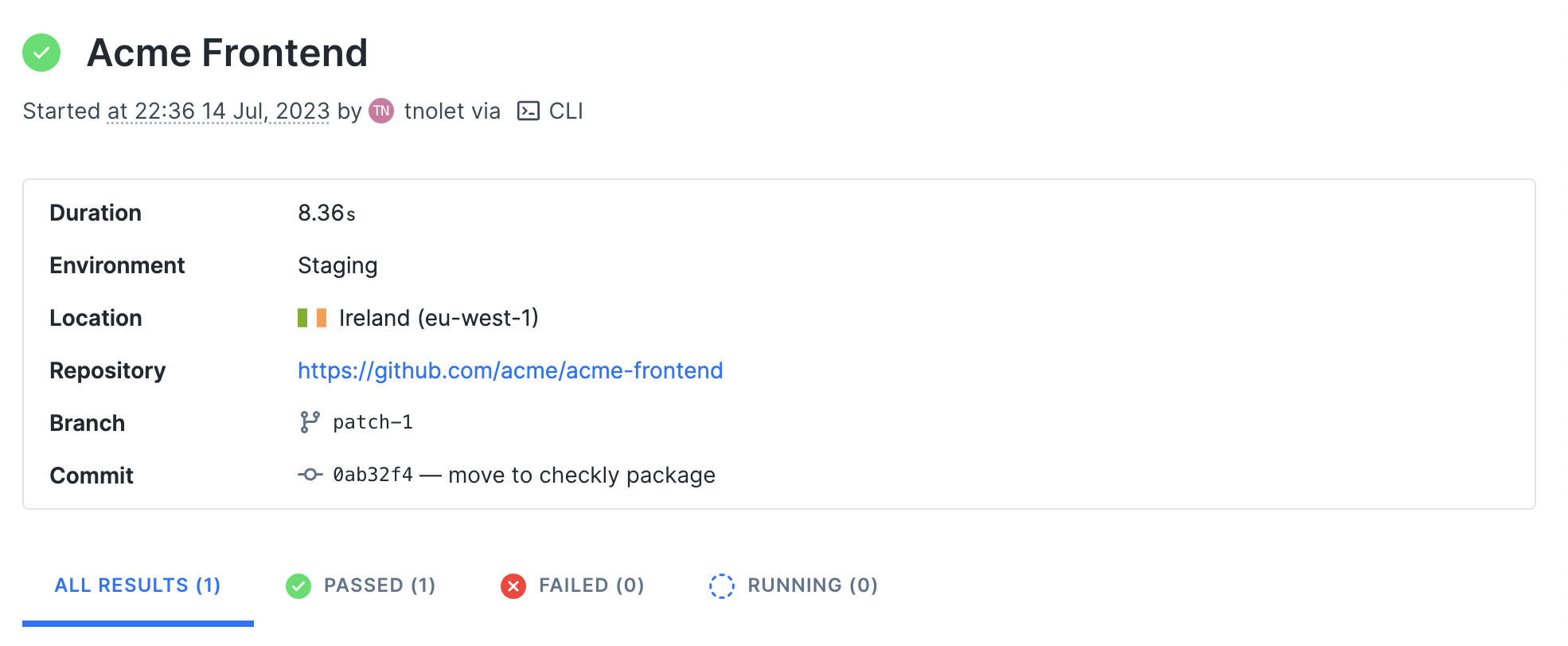
After the test succeeds, we deploy this check so it runs as a monitor with npx checkly deploy.
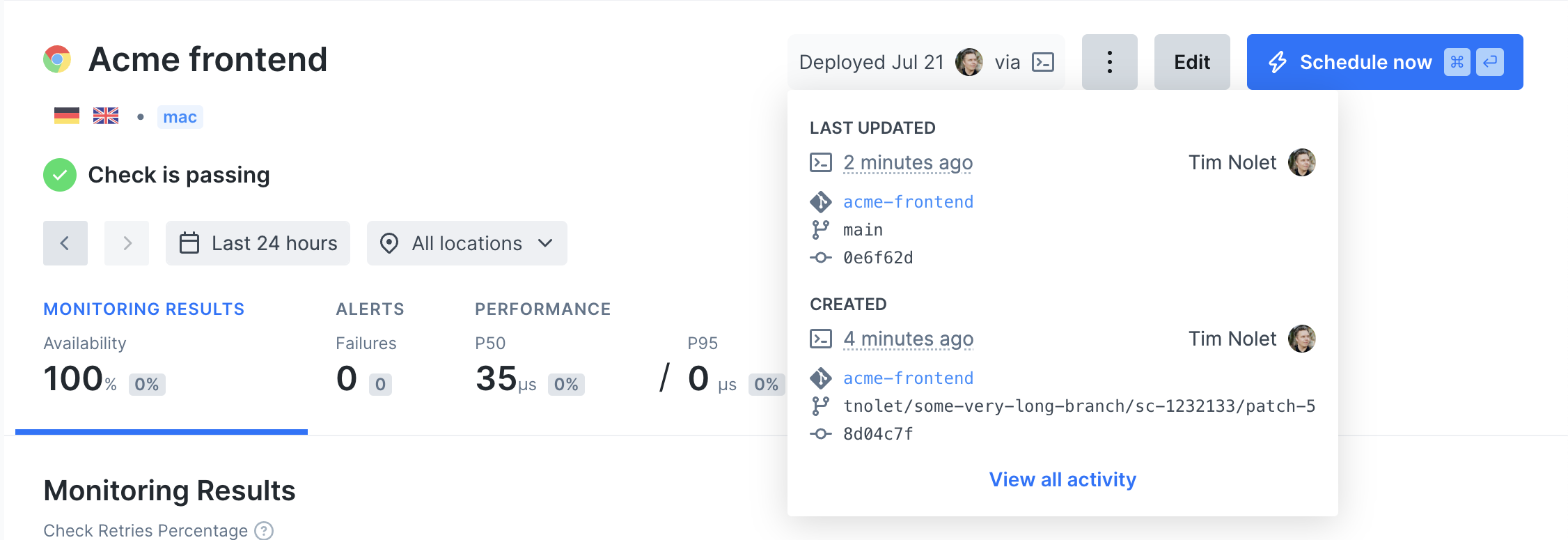
Environment variables
The CLI will attempt to auto-detect and parse git specific information from your local machine or CI environment, but you can also set these data items specifically by using environment variables.
| item | auto | variable | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Repository | false | repoUrl in checkly.config.ts or CHECKLY_REPO_URL |
The URL of your repo on GitHub, GitLab etc. |
| Commit hash | true | CHECKLY_REPO_SHA |
The SHA of the commit. |
| Branch | true | CHECKLY_REPO_BRANCH |
The branch name. |
| Commit owner | true | CHECKLY_REPO_COMMIT_OWNER |
The committer’s name or email. |
| Commit message | true | CHECKLY_REPO_COMMIT_MESSAGE |
The commit message. |
| Environment | false | CHECKLY_TEST_ENVIRONMENT |
The environment name, e.g. “staging” |
For example, if you want to specifically set the Environment you invoke:
CHECKLY_TEST_ENVIRONMENT=Production npx checkly test --record
Or, if you want to set repo URL you invoke:
CHECKLY_REPO_URL="https://my.git.solution/project/" npx checkly test --record
Last updated on December 2, 2024. You can contribute to this documentation by editing this page on Github